Yes, dogs can see color, but not like humans. They see a limited range of colors.
Their world is not just black and white, as many believe. While dogs can perceive some colors, their view is not as vibrant as ours. Dogs primarily see shades of blue and yellow. They lack the ability to see reds and greens like humans do.
This is because dogs have fewer types of color receptors in their eyes. Understanding how dogs see can help us interact better with them. It explains why certain toys attract them more. Knowing their color perception can also improve training methods. Dive into this fascinating topic to learn how a dog’s vision works. Discover the science behind their unique view of the world.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Canine Vision Basics
Ever wondered how your furry friend sees the world? Canine vision is a fascinating topic that reveals much about how dogs perceive their surroundings. Understanding the basics of canine vision can help you appreciate why your dog behaves the way it does. Let’s dive into the key aspects of how dogs see.
Eye Structure In Dogs
The anatomy of a dog’s eye is uniquely designed for their needs. Dogs have a larger cornea and lens compared to humans. This allows more light to enter, giving them better night vision. However, this means their vision is not as sharp during the day.
Their eyes also contain a special layer called the tapetum lucidum. This reflects light back through the retina, enhancing their ability to see in low-light conditions. It’s why your dog’s eyes might seem to glow in the dark.
Think about the last time your dog spotted something in the shadows before you did. Their eye structure is the reason they have a keen sense of vision in dim lighting.
Differences From Human Eyes
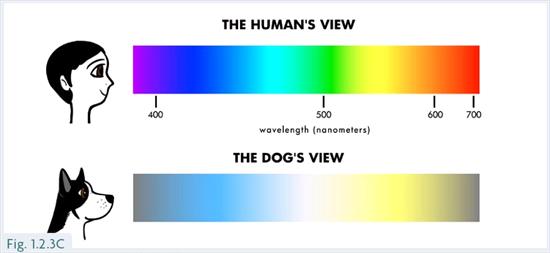
Dogs don’t see the world in the same vibrant colors that humans do. They are dichromatic, meaning they primarily see shades of blue and yellow. Red and green appear as shades of gray to them.
This difference is due to the number of cone cells in their eyes. Humans have three types of cones, while dogs have only two. This limits their color spectrum, affecting how they see objects.
Next time you’re playing fetch, notice how your dog picks up on the movement rather than the color of the ball. Their eyes are more attuned to detecting motion and contrasts than vibrant colors.
Does your dog sometimes ignore the brightly colored toy you bought? It might be because they can’t distinguish it from the surroundings. Understanding these differences can help you choose toys that stand out in their vision.
Knowing these basics gives you a glimpse into the canine world. How does this knowledge change your perspective on your dog’s behavior? Could it improve your interactions and the choices you make for them? Consider this next time you’re planning a fun activity with your furry companion.
Credit: cattledogpublishing.com
Color Perception In Dogs
Have you ever wondered how your dog perceives the world through its eyes? Color perception in dogs is a fascinating topic that can change the way you see your furry friend. While dogs don’t see the world in black and white, their color vision is quite different from ours.
Types Of Colors Dogs See
Dogs primarily see a world in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to a person who is red-green colorblind. This means your dog can distinguish between blues and yellows but may struggle with reds and greens.
Their vision is due to the presence of two types of color receptors, or cones, in their eyes. Humans have three types, allowing a broader spectrum of color detection. Your dog’s vision is specially adapted to detect movement and changes in brightness, which is perfect for their natural hunting instincts.
Comparing Dog And Human Color Vision
Imagine walking through a park filled with vibrant flowers. To you, the colors are vivid and varied. To your dog, however, many of these colors blend into similar hues. They might focus more on the movement of a squirrel or a ball rather than the colors around them.
While this might seem like a disadvantage, it’s actually quite the opposite. Dogs have superior night vision and can see much better in low-light conditions than humans. This is because their eyes have more rods, which are responsible for detecting light and movement.
Have you noticed how your dog can spot a ball in the grass even when you struggle to find it? This ability is thanks to their keen perception of movement rather than color. Next time you’re playing fetch, remember it’s not just the color of the ball that matters, but how it moves!
Does knowing about your dog’s color perception change how you might choose toys or play with them? Perhaps you’ll opt for more blue and yellow toys, knowing they’ll stand out more clearly. Embrace this new perspective and see how it enhances your bond with your pet.
Scientific Studies On Dog Vision
Have you ever wondered how your dog views the world? While we might take the vibrant colors of a sunset for granted, dogs experience a different visual reality. Scientific studies have shed light on how dogs perceive colors, revealing insights that are both fascinating and surprising. Understanding the nuances of canine vision can deepen your connection with your furry friend.
Research Methods Used
Researchers employ various methods to study dog vision. Behavioral tests are common, where dogs are trained to respond to different colored stimuli. By observing their reactions, scientists can gauge which colors dogs can detect. In addition, advanced techniques like electroretinography measure electrical responses in the retina, offering a glimpse into how dogs process visual information.
Another approach involves genetic studies. By examining the genes responsible for eye function, researchers can infer the color range visible to dogs. These methods combined provide a comprehensive understanding of canine color vision.
Key Findings On Dog Color Vision
Studies reveal that dogs don’t see the world as vividly as humans do. Their vision is similar to a person with red-green color blindness. Dogs mainly perceive shades of blue and yellow, while reds and greens appear as grays or browns. This is due to the number and type of cone cells in their eyes.
Interestingly, this doesn’t hinder their ability to navigate their surroundings. Dogs rely more on other senses, such as smell and hearing, to understand their environment. So, while your dog might not appreciate the colors of a rainbow, they have their own unique way of experiencing life.
Ever noticed how your dog seems to respond to blue toys more than red ones? This is a practical example of their color perception. Understanding these nuances can help you choose toys and accessories that are more appealing to your pet. Have you ever tried this with your dog? What was the outcome?

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Myths About Dog Vision
Contrary to popular belief, dogs can see color. They perceive blue and yellow shades, but not red. Their vision is similar to a human’s colorblind experience. Understanding this myth can help improve pet care and training.
Dogs have long been subjects of fascination when it comes to their visual perception. A common topic of discussion is whether dogs can see color. Over the years, several myths about dog vision have emerged, leading to widespread misconceptions. Let’s dive into some of these myths and uncover the truth.Common Misconceptions
Many people still believe that dogs see in black and white. This idea has been popularized by outdated studies and often repeated in stories and films. You might recall hearing this as a child, convincing you that your furry friend sees the world in grayscale. Another misconception is that dogs have poor vision overall. Some think dogs can’t see well in dim light or at a distance. This myth might stem from observing a dog bumping into things, but that behavior is often due to other factors, like excitement or age-related issues.Debunking Vision Myths
Contrary to the black-and-white myth, dogs can see color, albeit differently than humans. They perceive the world in shades of blue and yellow, lacking the ability to see reds and greens. This is similar to how a person with red-green color blindness views the world. Dogs have excellent night vision due to a higher number of light-sensitive cells in their eyes. So, if you notice your dog navigating effortlessly in low light, it’s because they see better in the dark than you do! It’s also a myth that dogs can’t see well at a distance. While their vision might be less sharp than ours, they compensate with heightened senses of smell and hearing. Remember, they’re adept hunters and trackers, relying on a combination of senses to understand their environment. Do these myths change how you view your dog’s abilities? Next time you watch your dog chase a toy, consider their unique perception of the world. Understanding these myths helps you appreciate the incredible ways dogs interact with their surroundings.Impact Of Vision On Dog Behavior
Dogs perceive the world differently, seeing shades of blue and yellow rather than a full spectrum. Their limited color vision influences behavior, aiding in detecting movement and navigating surroundings. Understanding this helps in training and enhancing their environment for comfort and interaction.
The Impact of Vision on Dog Behavior is more significant than you might think. Although dogs don’t perceive the world exactly as humans do, their unique vision still plays a crucial role in their daily activities and interactions. Understanding how dogs see can enhance your training techniques and improve your bond with them. ###Visual Cues In Dog Training
Using visual cues in training can be highly effective. Dogs are excellent at picking up on body language and gestures. By incorporating hand signals along with verbal commands, you can communicate more clearly with your furry friend. Imagine you’re teaching your dog to sit. Along with saying “sit,” you raise your hand in a specific motion. Over time, your dog will associate the hand movement with the action, even if they can’t hear you. Dogs also respond well to consistency. Using the same visual cues every time helps them learn faster and strengthens their obedience. Have you ever noticed your dog responding to a familiar gesture or even preparing to follow a command before you say it? That’s the power of visual cues in action. ###Color Influence On Dog Activities
Dogs see colors differently than humans, with a vision similar to a person who is colorblind. They can see shades of blue and yellow but not reds or greens. This color perception can influence the toys they prefer or how they engage with their environment. If you notice your dog ignoring a red ball, try offering a blue or yellow one. You may see an immediate change in their enthusiasm and engagement. This simple tweak can make playtime more enjoyable for both you and your pet. Think about the agility courses you might see in dog competitions. These often use blue or yellow equipment to ensure dogs can easily spot and navigate the obstacles. Could the colors in your dog’s environment be affecting their behavior and activity levels? Understanding your dog’s vision can lead to more effective training and a happier, more engaged pet. What changes will you make today to align better with your dog’s unique view of the world?Enhancing Dogs’ Visual Experience
Understanding how dogs see the world can help you enhance their visual experience. Dogs perceive colors differently than humans. Instead of a rainbow spectrum, they primarily see shades of blue and yellow. By considering this, you can choose toys and design spaces that cater to their unique vision. This not only makes their environment more enjoyable but can also improve their overall well-being.
Choosing Toys Based On Vision
When selecting toys for your dog, consider their color perception. Bright blue and yellow toys stand out to them. These colors are more engaging and easier for dogs to distinguish.
Remember the last time you saw your dog ignore a red ball? Red appears as a dull gray to them. Opt for toys in colors they can see vividly. You’ll notice they interact more and have a better playtime experience.
Next time you’re shopping for dog toys, look for those that match their vision spectrum. This small change can make a big difference in their playtime enjoyment.
Designing Spaces For Dogs
Creating a dog-friendly space involves more than just comfort; it’s about visibility too. Use color schemes that align with their visual capabilities. Blue and yellow accents can make a space more inviting for your furry friend.
Think about how you can rearrange your living room. Use blue cushions or yellow rugs to catch their attention. This enhances their ability to navigate and feel more at home.
Consider lighting as well. Dogs may not appreciate as much brightness as humans do. Soft lighting can create a calming atmosphere, making them feel relaxed.
How can you transform your space to better suit your dog’s vision? Small adjustments can lead to a happier, more visually stimulating environment for them.
Vision Problems In Dogs
Dogs, like humans, can suffer from vision problems. These issues can affect their quality of life and may require attention. Understanding common eye disorders, their symptoms, and treatments can help you ensure your dog’s well-being.
Common Eye Disorders
Many dogs experience cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal diseases. Cataracts cause cloudiness in the eye and can lead to blindness. Glaucoma results from increased pressure in the eye and may cause pain. Retinal diseases affect the retina, leading to vision loss.
Symptoms And Treatments
Watch for signs such as redness, excessive tearing, and squinting. A dog may also bump into objects or show reluctance to move. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for early detection. Treatments vary; they may include medication or surgery.
Future Research Directions
Exploring how dogs perceive color opens exciting research paths. Scientists aim to uncover the range of colors dogs see. Understanding this can deepen the bond between humans and dogs.
Dogs have always been fascinating creatures, especially when it comes to their vision. While we know that dogs see the world differently than humans, the journey to fully understanding their color perception is far from over. Researchers are continuously exploring new avenues to gain more insights into how our furry friends perceive colors, and the future holds exciting possibilities.Advancements In Vision Studies
Recent studies have made significant strides in understanding canine vision. Scientists are now using advanced imaging technology to observe the dog’s eye structure in greater detail. This technology could lead to breakthroughs in identifying specific cells responsible for color detection. In addition to imaging, genetic research is also on the rise. By analyzing canine DNA, researchers hope to identify genes that influence color vision. This could pave the way for more targeted studies and treatments for vision impairments in dogs.Potential Discoveries In Canine Vision
What if dogs perceive colors we can’t even imagine? Future research may reveal unexpected aspects of canine color vision. These findings could challenge our understanding and lead to new theories about animal perception. Imagine if scientists discovered that certain breeds have unique color vision capabilities. This could change how we train, breed, and care for different types of dogs. Such discoveries might also influence how we design environments and toys for our pets. As research progresses, it’s essential for dog owners to stay informed. How will these discoveries affect your relationship with your pet? By understanding more about how dogs see the world, you can create a more enriching experience for them. The future of canine vision research is bright and full of promise. By keeping an open mind and staying updated, you can be part of this exciting journey. What new insights will the next decade bring about how dogs perceive their world?Frequently Asked Questions
What Colors Do Dogs See Best?
Dogs see blue and yellow colors best. Their vision is similar to a human with red-green color blindness. They perceive shades of blue and yellow more vividly, while reds and greens appear as grayish tones. This color perception helps them detect motion and navigate their environment effectively.
Do Dogs See In Black Or White?
Dogs do not see in black and white. They perceive colors, but differently from humans. They see shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to a person with red-green color blindness. This is due to having only two types of color receptors in their eyes.
What Color Can Dogs See In Grass?
Dogs see grass primarily in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to red-green color blindness in humans. They can’t see the full spectrum of colors humans do. Grass appears as a blend of muted colors to them.
What Does A Dog’s Vision Look Like?
Dogs see the world mainly in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to a human with red-green color blindness. Dogs have better motion detection and night vision due to more rod cells in their retinas. Their field of view is wider, but they perceive less depth.
Conclusion
Dogs see colors differently than humans. Their world is not black and white. Dogs perceive shades of blue and yellow. This is because of their two color receptors. Humans have three, giving us a wider color range. Dogs excel in detecting motion and seeing in dim light.
Their vision suits their natural needs. Understanding canine color vision helps us care for them better. It enhances our bond with these loyal companions. Dogs may not see all colors, but they see what matters. In their eyes, life is vibrant in its own way.

