Yes, dogs can see color, but differently than humans. They perceive a limited spectrum.
Their world is mostly in shades of blue and yellow. This topic often intrigues pet owners and animal enthusiasts alike. Dogs experience the world visually in a unique way, unlike humans. While we enjoy a colorful spectrum, dogs have a different set of visual capabilities.
Their eyes have fewer color receptors, which affects their perception of hues. Understanding how dogs see color can enhance our interaction with them. It helps in choosing toys and creating environments they enjoy. By knowing their visual limits, we can improve their experiences. This knowledge not only fascinates but also aids in bettering canine care. Dive into the science behind a dog’s vision and discover the colorful truth.
Canine Vision Basics
Understanding canine vision helps us connect better with our furry friends. Dogs perceive the world differently through their eyes. Their vision is tailored to their needs and instincts. Exploring the structure of dog eyes and differences from human vision reveals fascinating insights.
Structure Of Dog Eyes
Dog eyes have a unique design suited for their lifestyle. The retina contains two types of cells: rods and cones. Rods help dogs see in low light. Cones allow them to see color, but with limitations. Dogs have fewer cones than humans. This affects their color perception.
The position of a dog’s eyes gives them a wide field of view. This is essential for spotting movement and potential threats. Their eyes are more adapted for night vision. This is due to the high number of rods and a special layer called the tapetum lucidum.
Differences From Human Vision
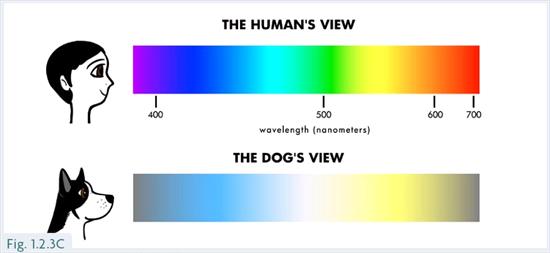
Human eyes perceive a wide range of colors. Dogs see fewer colors due to fewer cones. They mainly see shades of blue and yellow. Red and green appear as shades of gray to them.
Humans rely heavily on visual cues. Dogs depend more on smell and sound. Their vision suits their hunting and survival instincts. Dogs have a better ability to detect motion. This helps them spot prey or play with agility.
Understanding these differences helps us train and interact with dogs better. It also explains why dogs react differently to visual stimuli.
Credit: cattledogpublishing.com
Color Perception In Dogs
Dogs see the world differently than humans. Their color vision is less vivid. Dogs perceive colors, but not like humans. Their eyes have fewer color receptors. This affects how they see the world. Understanding this can deepen our bond with them.
Colors Dogs Can Detect
Dogs mainly see blue and yellow. They cannot see red or green. These colors appear as shades of gray. The world to a dog is more muted. Blue stands out brightly. Yellow is also clear. This limited color range shapes their view.
Comparing To Human Color Vision
Humans have three types of color receptors. Dogs only have two. This makes human vision richer in color. We see a full spectrum. Dogs see fewer colors. Their vision resembles a colorblind human’s vision. It’s more about brightness and contrast for them.
Scientific Studies On Dog Vision
Understanding how dogs perceive the world has intrigued scientists for years. Their ability to see colors differently from humans raises fascinating questions. Research on dog vision helps us understand their unique visual capabilities. Numerous studies have explored the complexities of canine vision. These studies reveal intriguing insights into how dogs see colors.
Key Research Findings
Scientists discovered dogs see fewer colors than humans. Dogs can see shades of blue and yellow. They struggle to differentiate between red and green. This limited color spectrum affects their perception. Dogs rely on other senses to navigate their environment. Their vision is adapted to their specific needs.
Methodologies Used In Studies
Researchers employed various methods to study dog vision. Behavioral tests are common in these studies. Dogs are presented with colored stimuli. Their responses are observed and recorded. Visual cues and rewards help gauge their perception. Advanced imaging techniques like electroretinography are also used. This helps analyze the retinal responses of dogs to different colors. These methodologies provide comprehensive insights into canine vision.
Impact Of Color Vision On Dog Behavior
Dogs see the world differently than humans. Their color vision impacts behavior. They perceive fewer colors, mostly blues and yellows. This influences how they interact with their environment. Understanding this can help improve play and training sessions. It also affects their hunting and tracking abilities.
Influence On Play And Training
Dogs love to play with toys. Brightly colored toys can be hard for them to see. Toys in blue or yellow stand out more. This can keep them engaged longer. Training with these colors can enhance focus. Dogs might respond better to commands when using blue or yellow items. This helps in teaching new tricks efficiently.
Effects On Hunting And Tracking
Color vision plays a role in hunting. Dogs rely on motion and scent more than color. They can spot a moving object better than a static one. This aids in tracking prey. Their ability to see some colors helps in distinguishing environments. This can make them better at tracking scents in different terrains. Understanding their color vision can aid in training hunting dogs.
Common Myths About Dog Vision
Dogs have fascinated humans for centuries, especially regarding their vision. Many myths surround how dogs see the world. Let’s explore some common misconceptions about dog vision.
Debunking Full Colorblindness
A popular myth claims dogs see only black and white. This myth is not true. Dogs can see colors, but differently than humans. They perceive the world in shades of blue and yellow. Their color vision is like a human’s with red-green colorblindness.
This means red and green appear as shades of gray. But blue and yellow are vivid to them. Next time you choose a toy, consider its color. Your dog will appreciate the right hues.
Misconceptions About Night Vision
People often think dogs have super night vision. Dogs do see better in the dark than humans. Their eyes have more rod cells, which detect light. But they don’t see in complete darkness.
Dogs also have a reflective layer behind their retina. This layer helps them use limited light more effectively. While they see better in dim light, they need some illumination. Dogs rely on other senses, like smell, to navigate in the dark.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Practical Implications For Dog Owners
Understanding that dogs see colors differently can affect daily choices. Dog owners can make informed decisions to enhance their pet’s environment. Recognizing these implications can improve a dog’s quality of life.
Choosing Toys And Accessories
Dogs distinguish blue and yellow hues easily. Choosing toys in these colors can make playtime engaging. Avoid red toys as dogs find them hard to see. Opt for bright blue or yellow accessories. This choice helps dogs recognize and interact with their playthings.
When selecting collars or leashes, consider visibility. Bright colors are better for outdoor use. They enhance safety and visibility during walks. Choose gear that stands out against the surroundings.
Designing Dog-friendly Spaces
Designing spaces with color in mind can benefit your dog. Use blue or yellow for walls or furniture accents. These colors are visible to dogs and can make spaces appealing. Avoid reds and greens in areas your dog frequents. They may not stand out for your pet.
Lighting plays a role in color visibility. Ensure spaces are well-lit for your dog to see clearly. Natural light can enhance color differentiation. Consider window placements and light fixtures. These elements improve your dog’s environment.
Enhancing Dog’s Visual Experiences
Dogs see the world differently than humans. They view colors in a unique way. While humans see a rainbow of colors, dogs see shades of blue and yellow. This doesn’t mean their world is dull. We can enhance their visual experience with simple changes.
Stimulating Environments
Creating a stimulating environment can enrich a dog’s life. Bright toys in blue and yellow can capture their attention. These colors stand out to dogs. Place these toys in different areas. This encourages exploration and play. Use contrasting colors for bedding and bowls. It makes these items easy for dogs to find.
Gardens with blue and yellow flowers can also stimulate dogs. These colors are vibrant to them. A colorful backyard can be a paradise. It provides visual interest and joy.
Using Color In Training
Colors can play a role in training sessions. Use blue or yellow objects for training cues. These colors are easy for dogs to see. Brightly colored training tools can enhance focus. It makes learning more effective.
For example, a blue ball for fetch is easier to spot. This keeps the dog’s attention on the task. Use yellow markers for agility courses. It guides the dog more clearly. Training becomes more engaging with the right colors.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Future Directions In Canine Vision Research
The world of canine vision research is ever-evolving, offering fresh insights that challenge long-held beliefs. As technology advances, scientists are better equipped to understand how dogs perceive the world. This ongoing research could change how we interact with our furry friends and even improve their quality of life. But what does the future hold for this fascinating field? Let’s dive into the possible future directions in canine vision research.
Advancements In Technology
New technologies are opening up exciting possibilities in canine vision research. Researchers now use advanced imaging techniques to study a dog’s eye structure in unprecedented detail. These tools help identify specific visual capabilities and limitations in dogs, leading to a clearer understanding of their color perception.
Wearable tech is another promising area, offering real-time data on how dogs interact with their environment. Imagine a device that could record what colors your dog sees during a walk in the park. This information could help pet owners provide a more enriching experience for their dogs.
Potential Breakthroughs
Scientists are exploring genetic factors that influence canine vision, which could lead to groundbreaking discoveries. By identifying specific genes related to color vision, researchers might develop therapies to enhance vision in dogs with deficiencies.
Another potential breakthrough involves training dogs to communicate their color perception. Imagine a future where dogs can signal a preference for certain colors through trained responses. This could revolutionize how we understand and cater to their needs.
Are you curious about how these advancements could change the way we care for our pets? The future might hold answers that enhance the bond between you and your canine companion. With each discovery, we come closer to seeing the world through their eyes, offering a richer, more connected experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Colors Do Dogs See Best?
Dogs see best in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to red-green color blindness in humans. They struggle with distinguishing reds and greens. Their eyes are adapted for low-light conditions, enhancing their ability to see in the dark.
This makes them excellent at detecting motion.
Do Dogs See In Black Or White?
Dogs don’t see in black and white; they see in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is limited compared to humans, lacking red and green hues. This is due to having fewer color-detecting cones in their eyes. Understanding dog vision helps improve their environment and activities.
What Color Can Dogs See In Grass?
Dogs see grass in shades of yellow and blue. Their vision is limited compared to humans. They lack red and green cone receptors, making their color perception different. While humans see vibrant greens, dogs experience a muted palette. This is due to their dichromatic vision system.
What Does A Dog’s Vision Look Like?
Dogs see the world mostly in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision lacks red and green colors. They have better motion detection and night vision than humans. Dogs can perceive some depth and detail, but their vision is less sharp.
They rely heavily on other senses like smell and hearing.
Conclusion
Dogs see colors differently than humans. Their world is less colorful. Dogs primarily see shades of blue and yellow. Red and green look gray to them. This unique vision helps dogs in low light. Their sight adapts well to dusk.
Understanding dog vision aids better interaction. It helps in choosing dog toys. Opt for blue or yellow toys. These colors stand out to them. Knowing this enhances playtime. Dogs perceive colors uniquely. This makes them special. Embrace their colorful world.
It’s fascinating to explore. Dogs’ vision is truly remarkable. It adds charm to our bond with them.

