Dogs do see colors, but not like humans do. They perceive a limited color spectrum.
Their world is mostly seen in shades of blue and yellow. This raises a fascinating question about how dogs view the world around them. Understanding how dogs see can help us improve their environment and activities. It might surprise you to learn that dogs don’t see the vibrant reds or deep greens we do.
Instead, their vision is more about contrasts and movement. This color limitation doesn’t hinder their daily life. Dogs rely more on smell and hearing. Their unique vision adapts perfectly to their needs. By exploring how dogs see colors, we can better appreciate their experiences and interactions with the world.
Canine Vision Basics
Understanding canine vision can enhance how we interact with dogs. Dogs see the world differently. Their vision is tailored to their needs as hunters and companions. This section explores the basics of how dogs perceive color and light.
Anatomy Of Dog Eyes
Dog eyes are structured uniquely. They have a larger pupil size than humans. This allows them to capture more light. Their eyes contain fewer cone cells. Cone cells are responsible for color vision. Instead, dogs have more rod cells. Rod cells help them see better in low light.
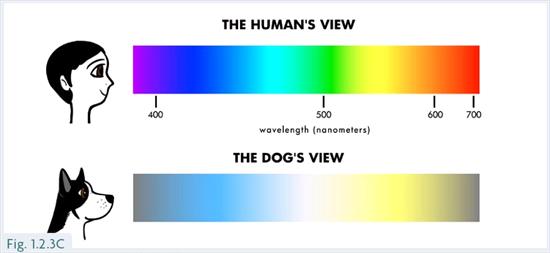
Comparative Vision With Humans
Dogs and humans don’t see the same color range. Humans have three types of cones. This enables us to see a full spectrum of colors. Dogs only have two types of cones. They primarily see shades of blue and yellow. Colors like red and green appear grayish to them.
Dogs excel in detecting motion. Their peripheral vision is superior. This helps them spot movement quickly. Night vision is also better in dogs. Their eyes adapt faster to darkness.
Credit: cattledogpublishing.com
Color Perception In Dogs
Have you ever wondered how dogs perceive the world around them, especially when it comes to colors? While many of us assume that our furry friends see in black and white, their color vision is more nuanced than that. Understanding color perception in dogs can help you choose toys, plan activities, and even decorate your home in ways that are more appealing to them.
Color Range Dogs Can See
Unlike humans, who see a wide spectrum of colors, dogs have a more limited color range. They primarily see shades of blue and yellow. This is due to the types of photoreceptors in their eyes.
Imagine looking through a pair of sunglasses with a yellow tint. That’s somewhat similar to how dogs perceive the world. Red and green hues appear grayish or brown to them, so that bright red ball might not be as eye-catching to your dog as you think.
Role Of Cone Cells
The secret behind color vision lies in cone cells, which are light-sensitive cells in the retina. Humans have three types of cone cells, allowing us to see a broad spectrum of colors. Dogs, however, have only two types of cone cells.
These two types of cone cells limit their ability to differentiate between certain colors. This doesn’t mean they see the world in dull tones. They still enjoy a vibrant world, just different from ours. Next time you pick out a new toy, consider one in blue or yellow to capture their attention.
Have you ever noticed how your dog goes wild for that yellow ball, ignoring the red toy right beside it? You might now understand why! Understanding your dog’s color perception could change the way you interact with them daily.
Have you adapted your choices based on your dog’s color vision? How has it changed your pet’s playtime experience? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
Myths About Dog Vision
Dogs see color, but not as humans do. Their vision includes shades of blue and yellow. It’s a myth that they see only in black and white. Understanding this can help in choosing the right toys and training tools.
Myths About Dog Vision
Dog vision is a topic surrounded by myths and misconceptions. Many people believe dogs see the world in black and white, but that isn’t entirely true. Understanding how dogs perceive color can help us better care for our canine companions.
Common Misconceptions
It’s common to hear that dogs are completely colorblind, only seeing in shades of gray. This myth likely stems from an outdated belief that dogs have the same vision as early black-and-white televisions.
Another misconception is that dogs see the world like we do, but in a sepia tone. This oversimplifies their unique color perception. Dogs actually have a different spectrum of vision.
Think about this next time you choose toys for your dog. Bright reds and oranges might not stand out as much as you think. Dogs may struggle to distinguish these from the grass or ground.
Scientific Findings
Research has shown that dogs can see some colors, but not the full spectrum humans do. They mostly perceive blues and yellows, akin to a person with red-green color blindness. This is due to the different types of cones in their eyes.
Dogs have two types of cones compared to three in humans. This limits their ability to discern between certain colors, like reds and greens, which might appear more as shades of gray or brown.
When playing fetch, your dog might have an easier time spotting a blue ball than a red one. This insight can make playtime more engaging for your furry friend.
Have you ever wondered why your dog seems to notice movement more than still objects? Their eyes are adapted to detect motion, a crucial trait for hunting and survival.
Incorporating these findings into your dog’s daily life can enrich their experiences. Choose toys and accessories in colors they can see better. Engage them with activities that play to their strengths in motion detection.
So, next time you’re picking out a new toy or planning an activity, consider how your dog sees the world. You’ll be amazed at how a small change can make a big difference in their enjoyment and interaction.
Impact Of Color On Dog Behavior
Dogs have a unique way of perceiving the world, and color plays a role in shaping their behavior. Although they don’t see the full spectrum like humans, the colors they can see still impact how they interact with their environment. Understanding this can help you train and care for your dog better. Ever noticed your dog reacting differently to objects of different colors? This might not be a coincidence.
Color Influence On Training
Colors can be a useful tool in dog training. Red and green might seem similar to your dog, so stick to blue and yellow toys for easier recognition. Dogs tend to respond better to these colors during training sessions. You might find that using a brightly colored toy can keep your dog more focused. Have you tried changing the color of your training tools?
Color Preference In Dogs
Do dogs have favorite colors? Some studies suggest they might prefer certain hues. Dogs often show a liking for blue and yellow, as these are among the colors they can see clearly. You might notice your dog frequently choosing toys of these colors. This preference can be used to make playtime more enjoyable. Why not experiment with different colored items to find your dog’s favorite?
Research On Canine Color Vision
Understanding how dogs perceive the world is a fascinating journey into the realm of canine color vision. Have you ever wondered what colors your furry friend can actually see? Research on canine color vision has evolved significantly over the years, shedding light on how dogs interpret their vibrant surroundings. Let’s dive into some of the key studies and technological advances that have shaped our understanding of how dogs see color.
Key Studies In Animal Vision
Research on animal vision, including dogs, has been ongoing for decades. In a groundbreaking study, scientists discovered that dogs have two types of color receptors, known as cones, in their eyes. This means they perceive colors differently from humans, who have three types of cones.
Another important study found that dogs see the world in shades of blue and yellow. This differs from the wide spectrum of colors humans can see. Imagine a rainbow through a dog’s eyes—it’s a lot simpler, yet still beautiful.
These studies provide a glimpse into the dog’s visual world. They help us understand why dogs might not react to certain colors the way we do.
Technological Advances
Technological advances have played a crucial role in deepening our understanding of canine vision. Modern imaging technologies, like retinal scans, allow scientists to observe the structure of a dog’s eye in detail.
These technologies have confirmed the presence of two types of cones in dogs’ eyes. They have also helped researchers develop tools to test how dogs react to different colors and light intensities.
Additionally, apps and devices are being developed that simulate dog vision for humans. These tools help pet owners choose toys and accessories that appeal to their dog’s visual preferences.
Have you ever used one of these apps to see the world through your dog’s eyes? It offers a unique perspective and can enhance how you interact with your pet.
Understanding canine color vision isn’t just about science. It’s about improving the bond between you and your dog. By learning what colors your dog can see, you can make choices that enrich their life. So, what colorful surprises will you explore with your dog today?
Practical Implications For Owners
Many dog owners wonder about their pets’ color vision. Understanding this can help in daily life. Dogs see a limited range of colors. They see shades of blue and yellow. This affects how they interact with their environment. Knowing this helps owners make better choices for their pets. Below, we explore practical implications for dog owners.
Choosing Toys And Accessories
Bright colors like red or green won’t stand out to dogs. Opt for blue or yellow toys. These are easier for dogs to see. Picking the right color can make playtime more fun. It also helps dogs find toys quickly. Blue and yellow collars or leashes are good choices too. These colors are more visible to dogs during walks.
Designing Dog-friendly Spaces
Color choices affect how dogs navigate spaces. Use blue or yellow accents in play areas. This can encourage dogs to explore more. Paint walls or choose rugs in these colors. It makes spaces more inviting for your dog. A comfortable space boosts their mood. It also enhances their overall well-being.
Comparative Vision In Other Animals
Understanding how different animals perceive color is fascinating. Each species sees the world in its unique way. While humans enjoy a wide spectrum of colors, animals differ significantly. This section explores the vision in cats and wild animals.
Color Vision In Cats
Cats have limited color vision compared to humans. They mainly see shades of blue and green. Red and pink appear as shades of gray to them. Their eyes are designed for night vision. This means they see better in dim light. Their retinas contain more rod cells than cone cells. Rod cells are sensitive to light and help in low-light conditions.
Vision In Wild Animals
Wild animals have diverse visual capabilities. Birds have exceptional color vision. They see ultraviolet light, which humans cannot. This helps them find food and mates. Bees also see ultraviolet light. This guides them to flowers for pollination.
Deer have dichromatic vision like dogs. They see shades of blue and yellow well. Their vision helps them detect predators. Predators such as lions have eyes suited for tracking movement. Their vision aids in hunting even in low light.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Future Exploration In Canine Vision
Exploring canine vision reveals fascinating insights into how dogs perceive colors. Unlike humans, dogs primarily see shades of blue and yellow. Understanding this can enhance training and interaction with them.
### Future Exploration in Canine Vision
As we continue to understand the world of our furry friends, the future of exploring canine vision holds exciting potential. Scientists are keen to uncover more about how dogs perceive colors and what this means for their interaction with the world. This journey not only helps us understand dogs better but also improves how we care for them.
###
Potential Studies
Imagine a study where dogs are shown different colored objects to gauge their reactions. Researchers could use advanced imaging technology to map out the canine visual spectrum. This would give us a clearer picture of their color perception.
Another potential study could focus on how environmental factors affect a dog’s ability to see colors. Do certain lighting conditions enhance or impair their color vision? Understanding these elements could lead to breakthroughs in designing dog-friendly environments.
###
Impact Of Findings On Dog Care
If studies reveal that dogs see specific colors better, think about how this could change dog toys and accessories. You might choose colors that are more stimulating for your dog, enhancing their playtime experience.
Knowing more about canine vision could also influence training techniques. Trainers might use colors dogs can see best to improve learning and command recognition.
This knowledge may even influence veterinary care. If dogs show signs of vision impairment, vets could use these findings to diagnose and treat issues more effectively.
Are there ways you could improve your dog’s environment based on what they see? Future research might just hold the key.

Credit: spca.bc.ca
Frequently Asked Questions
What Colors Do Dogs See Best?
Dogs see best in shades of blue and yellow. Their vision is similar to a human with red-green color blindness. They perceive the world in a limited color spectrum, primarily blues and yellows. This makes toys and objects in these colors more visible to them.
Do Dogs See In Black Or White?
Dogs don’t see in black and white. They perceive colors differently than humans, seeing shades of blue and yellow. Their vision lacks red and green, creating a limited color spectrum. Despite this, dogs rely more on motion and contrast for vision.
Their eyesight is adapted for low-light conditions.
What Color Can Dogs See In Grass?
Dogs see shades of yellow and blue in grass. They have a dichromatic vision. Their eyes lack red receptors, limiting their color perception. Grass appears mostly yellowish-green to them, unlike the vibrant green humans perceive. This unique vision helps them detect movement and contrast in their environment.
What Does A Dog’s Vision Look Like?
Dogs see the world in shades of blue and yellow, lacking full color vision. Their vision is slightly blurred, with a superior ability to detect movement. Dogs have better night vision due to more rod cells in their eyes, allowing them to see well in low-light conditions.
Conclusion
Dogs don’t see colors as humans do. They see shades of blue and yellow. Their world is not entirely black and white. This unique vision helps them spot movement. Understand their visual limits. This knowledge can help improve their lives.
Choose toys with contrasting colors. Pick environments with visible contrasts. Knowing their color perception can enhance interactions. It strengthens your bond with them. Dogs rely on smell and sound more. But understanding their vision aids communication. This insight bridges the gap between human and canine.
It fosters better companionship and care.

